MATH 100 SECTION 1 SECOND BLOCK: CORE MATERIAL
BASIC CONCEPTS: apportionment and voting. For a list of
basic concepts
see the lists of “Key Concepts” for Chapters 1 and 4 of Tannenbaum (on pages
29 and 144). You are not of course responsible for the material in section 1.6
on ranking (so you can ignore the key concepts on page 29 that have the word
“ranking” in them).
BASIC CONCEPTS: rational and irrational numbers.
rational number, irrational number, repeating decimal, nonrepeating decimal,
even and odd integers, right triangles
BASIC FACTS
1. The fundamental theorem of arithmetic (= the unique factorization theorem):
Every composite number can be written as a product of primes in
exactly one way (except for the order of the factors).
2. the Pythagorean theorem (page 58 of Stein)
3. theorems 1, 3, 4, 5, 6 on pages 63–66 of Stein
4. the rationality or irrationality of sums and products of rational and
irrational
numbers
5. a product of odd integers is odd (so if a product of integers is even, then
at least one must be even)
6. For any natural number N, we have 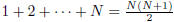
7. In an election with N alternatives, the total number of pairwise comparisons
is 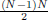 .
.
8. with t candidates the number of distinct possible preference ballots is
t! = 1 × 2 × 3 × · · · × t
9. The Arrow impossibility theorem
10. the Balinski and Young impossibility theorem
11. history of apportionment in the house of representatives
SOME BASIC COMPUTATIONS
Finding the decimal form of a rational number and writing a repeating decimal
as a quotient of integers.